What is Bursitis of the Shoulder?
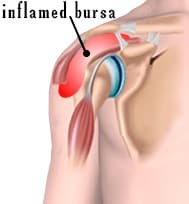 When someone is experiencing bursitis of the shoulder, pain, and tenderness surrounding the shoulder. This is especially the case when raising an arm above the head. It occurs when bursa sacs near the top of the shoulder become inflamed and enlarged.
When someone is experiencing bursitis of the shoulder, pain, and tenderness surrounding the shoulder. This is especially the case when raising an arm above the head. It occurs when bursa sacs near the top of the shoulder become inflamed and enlarged.
It’s common for someone who has shoulder bursitis to also have shoulder impingement syndrome. Since the soft tissue of the shoulder are so close together, when health problems occur with one, the other also has issues. Therefore, if one becomes injured, the other is also likely to be damaged.
Symptoms of Shoulder Bursitis
When bursitis first occurs shoulder pain is the most common symptom. This will happen on the outside of the shoulder.
Shoulder bursitis symptoms are normally one or more of the following:
- Shoulder pain
- Repetitive shoulder activity worsens pain
- Tenderness of the shoulder
- Fever
- Tiredness
- Radiating pain
- Weakened muscle
- Difficulty reaching behind the back
- Warm redness at shoulder
Causes & Risks of Bursitis
Although injuries and overuse are the most common cause, there are other causes that may be the reason for your shoulder pain, such as:
- Repetitive pressure on the shoulder.
- Shoulder injury or trauma.
- The elderly are more likely to get this disease, although any age can be affected.
- Bad posture decreases space between the acromion and the glenohumeral joint, making it more likely that the soft tissue in between will become squeezed and irritated.
- Bacterial infection of the bursa.
- Those who had bursitis in the past are more likely to have a recurrence.
- Bone spurs can cause irritation of the bursa.
Treatment for Bursitis of the Shoulder
It’s common for bursitis of the shoulder to be treated with home remedies. However, patients often like to refer to a doctor, such as an orthopedic for recommendations. Often symptoms are relieved by using the RICE method, rest, ice, compression, and elevation.
Additional treatment methods are commonly used, such as:
- Anti-inflammatories. Aspirin or ibuprofen can reduce swelling and discomfort in the shoulder.
- Rest. Reducing shoulder movement can stop the bursa from getting more irritated and give it time to heal. A shoulder brace can help. Along with rest, some gentle shoulder exercises can stop the joint from becoming stiff.
- Ice packs. When an injury or overuse causes bursitis, an ice pack can help within the first 5 days. Apply ice every 15 – 20 minutes at 4 – 6 hour intervals for pain relief and swelling.
- Steroid injections. If symptoms persist, a doctor can inject corticosteroids in or around the bursa. This reduces swelling and discomfort. The effects may be temporary, but treatment can be repeated several times.
Furthermore, surgical options become available after 6 – 12 months of conservative methods not responding. This is normally suggested as a last option. This procedure will repair the damage and also reduce pressure in the bursa.
