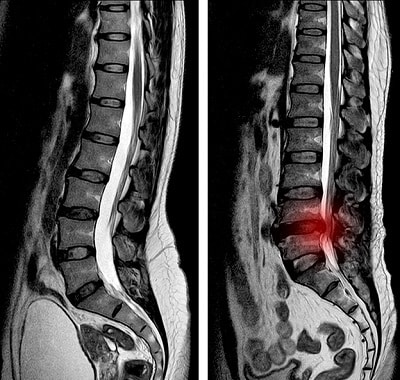
What is a Collapsed Disc?
A collapsed disc is a spinal disc that has lost its normal height due to deterioration of its fibrous outer wall. While this degeneration can be related to traumatic injury, it is commonly a result of wear due to the natural aging process.
A diminished disc height is most common within the cervical (upper) and lumbar (lower) regions of the spine, where the vertebrae bear significant body weight and are subjected to a wide range of stress-inducing motion.
A collapsed disc does not necessarily produce symptoms, but if the reduced disc height leads to compression of a nerve root or the spinal cord, pain, tingling, numbness or muscle weakness can occur.
Collapsed discs are most common in the lumbar (lower) region of the spine, since this area is responsible for supporting the majority of a person’s weight. A collapsed disc in the lumbar region typically causes symptoms in the lower back, buttocks, legs and feet.
Symptoms
If neural tissue is not compressed, no symptoms are produced. When a disc collapses and causes compression of a spinal nerve or the spinal cord itself, you can experience a number of symptoms, including:
- Pain in the neck, back and/or extremities
- Weakness or complete loss of muscular function
- Tingling
- Numbness
- Muscle spasms
These symptoms vary in severity and directly relate to the severity of neural compression. Symptoms may be experienced in different parts of the body depending on the location of the compressed nerve.
A compressed nerve in the cervical (neck) region of the spine, for instance, may cause the above symptoms in the neck, shoulders, arms and hands, while a compressed nerve in the thoracic (middle) region of the spine may cause discomfort in the ribs and torso.
Collapsed Disc Causes
A collapsed disc can develop due a series of degenerative conditions, meaning conditions that develop as the spine naturally deteriorates and weakens with age. These degenerative conditions can include:
- Degenerative disc disease. As a person ages, the spinal discs can become weaker and lose water content. When this happens, the discs tend to lose height and the space between the vertebrae can become smaller.
- Herniated disc. This condition occurs when the jellylike interior of a disc pushes through a tear in the disc’s tough exterior. The tear can be caused by degenerative changes that occur as a person ages or as a result of traumatic injury.
- Bulging disc. The causes of a bulging disc are similar to those of a herniated disc. With this condition, however, the interior of the disc remains contained within the outer layer, but the disc becomes flattened and extends beyond its usual perimeter.
Other causes of a collapsed disc include sudden injury or trauma that causes the disc to flatten and change shape.
Collapsed Disc Treatment
Call us at anytime at 1-888-409-8006 and ask us about the Possible Treatments & Procedures for Compressed Discs.
Collapsed Disc Diagnosis
Anyone who experiences chronic pain or discomfort in their neck or back and thinks it may be due to a collapsed disc should visit a primary care physician to receive a proper diagnosis and a personalized treatment plan. During your office visit, a doctor will typically take the following steps to reach a diagnosis:
- Medical history evaluation
- Physical exam
- MRI
- CT scan
- X-ray
- Discography
- Blood tests
Collapsed Disc Treatment Options
Medications are an extremely common option for treating collapsed discs. Patients may consider over-the-counter medications from their local drugstore, or they may seek a prescription from their physician. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, narcotic painkillers and even antidepressants can all be an effective part of a collapsed disc treatment plan.
Along with medications, patients can also explore other conservative therapies, including: corticosteroid injections, heat and/or ice therapy, stretching, exercise and physical therapy, therapeutic massage.
If conservative methods fail to provide adequate symptom relief, a spine specialist may recommend surgery. At Spine & Orthopedic Center, we can help you determine which collapsed disc treatments would be best for your specific situation. If you’d like to schedule an initial consultation to learn more about minimally invasive surgical treatment for a collapsed disc, contact us at 888-409-8006.
