What is Knee Bursitis?
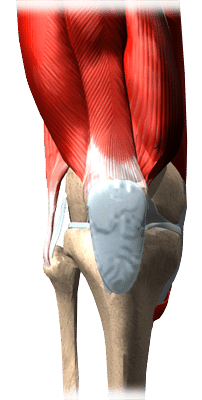
If you experience trauma, infection, or crystalline deposits, bursa sacs around the knee may become inflamed. Bursae act as cushions between the bones and tendons, reducing friction and cushioning pressure points near your joints. There are a few different types of knee bursitis that are in multiple parts of the knees.
One of the most common types of bursitis is known as prepatellar bursitis. This particular type of bursitis commonly occurs in people who work on their knees. Prepatellar bursitis is often referred to as housemaid’s knee or carpet layer’s knee.
Additionally, another type of knee bursitis is referred to as anserine bursitis. The anserine bursa is located just below the knee. This is most common in overweight women as well as athletes. Anserine bursitis will cause pain in the bursa and worsens with bending or while you sleep at night.
Knee bursitis not only causes pain but also limits your mobility.
Symptoms of Knee Bursitis
When you experience knee bursitis, symptoms may vary depending on which bursa is affected and the cause of the inflammation.
Typically, once a bursa is affected, you might feel tender, warm, and swollen when pressure is applied. At times, you might feel pain when you move around your daily activities or even during rest.
A hard hit to the knee will cause symptoms to arise quickly. Nonetheless, it is normal for symptoms to appear gradually. For instance, when irritation or friction is caused by a job that requires kneeling on hard surfaces. Which makes for symptoms to usually worsen over time.
Non-Surgical Treatment
It is typical for your physician to request imaging, such as X-rays, MRI, or even an ultrasound to help rule out injuries that appear to be similar to bursitis.
Often bursitis will improve on its own. However, depending on the affected area, your physician might recommend one or more of the following:
Medications: If the bursitis was originated from an infection, it is typical for your doctor to recommend an antibiotic.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy might alleviate pain and reduce the risk of a reoccurring injury through strengthening the surrounding muscles.
Surgical Treatment:
If you experience chronic or reoccurring bursitis and your body isn’t responding well to other treatments, your doctor will likely suggest surgery to remove the bursa.
If you are looking for a knee specialist, call us at 888-409-8006. Our top orthopedic surgeons are here to help.
