Suffering a labral tear can be a setback for athletes and active individuals. However, with proper treatment and rehabilitation, returning to sports and activities is possible. This article provides guidelines and considerations for safely resuming physical activities after a labral tear.
Understanding Labral Tears
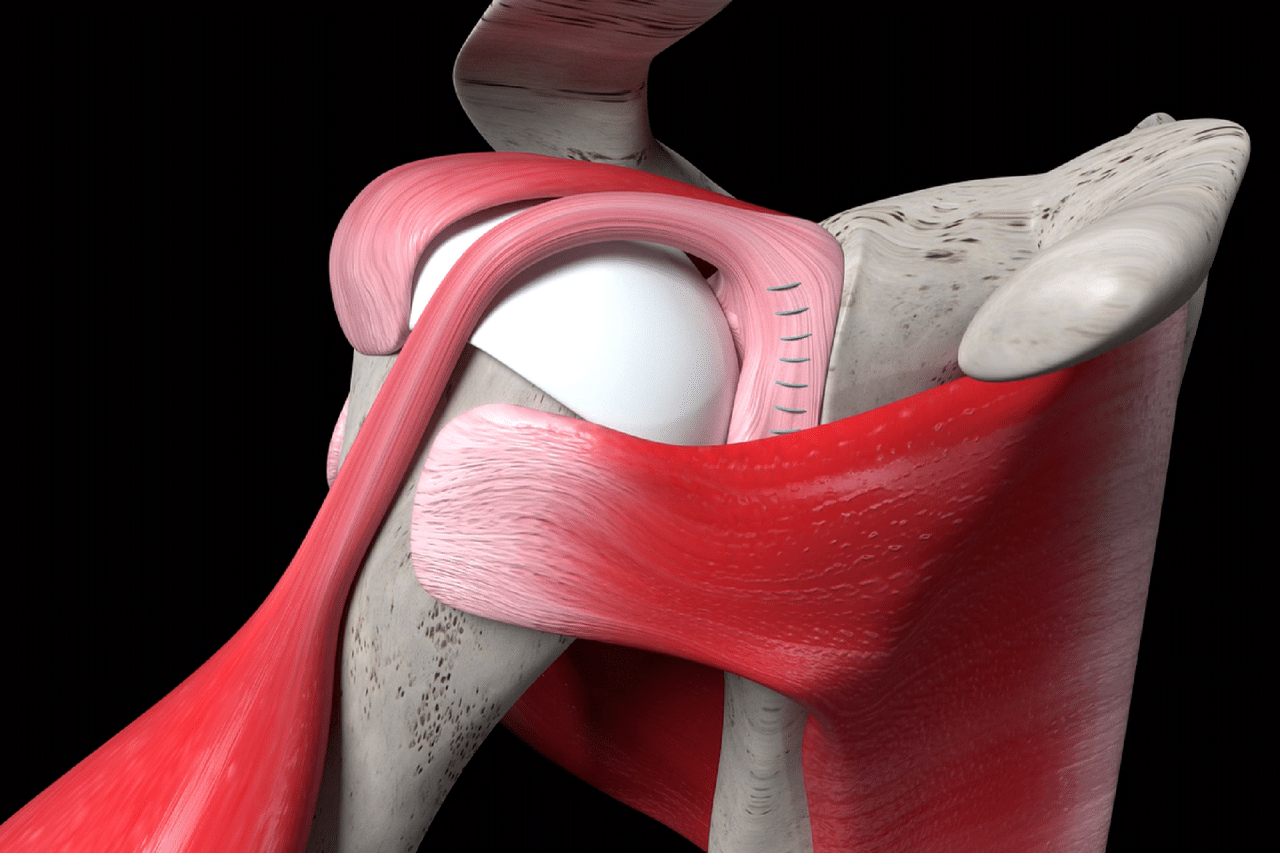
A labral tear is a common injury that affects the cartilage ring surrounding the shoulder or hip joint. It can result from trauma, repetitive motions, or degenerative conditions. The severity of the tear and individual factors influence the recovery timeline and return to activities.
- Follow Medical Guidance: Consult with a healthcare professional who specializes in orthopedic or sports medicine to evaluate the extent of the labral tear, discuss treatment options, and develop a personalized recovery plan.
- Conservative Treatment and Rehabilitation: Non-surgical treatment methods may be recommended for less severe labral tears. This can include physical therapy, pain management, and targeted exercises to strengthen the surrounding muscles and improve joint stability.
- Post-Surgical Rehabilitation: In cases where surgical intervention is necessary, rehabilitation plays a crucial role in the recovery process. Working closely with a physical therapist is essential to regain strength, flexibility, and proper movement patterns.
Returning to Sports and Activities
Returning to sports and activities after a labral tear requires a gradual and structured approach. Consider the following guidelines and considerations:
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any pain, discomfort, or limitations during and after activities. If you experience increased pain or other concerning symptoms, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider.
- Start with Low-Impact Activities: Begin with low-impact exercises and activities that put minimal stress on the injured joint. This may include swimming, stationary cycling, or gentle range-of-motion exercises.
- Progress Gradually: Gradually increase the intensity, duration, and complexity of activities as your strength and stability improve. Follow the guidance of your healthcare provider or physical therapist to ensure a safe and effective progression.
- Modify Techniques: Work with a qualified coach or instructor to modify techniques or movements that may put excessive stress on the injured joint. This can help reduce the risk of re-injury and promote proper biomechanics.
- Maintain Strength and Flexibility: Continue with targeted exercises and stretches that support the injured joint and improve overall strength and flexibility. This can help prevent future injuries and enhance performance.
- Consider Protective Measures: Depending on the sport or activity, wearing protective gear such as braces, padding, or taping may be recommended to provide additional support and stability to the injured joint.
Returning to sports and activities after a labral tear requires patience, proper medical guidance, and a structured rehabilitation program. It is crucial to follow the recommendations of healthcare professionals, gradually increase activity levels, and prioritize ongoing strength and flexibility training. By taking a cautious and thoughtful approach, individuals can safely resume their desired sports and activities, minimizing the risk of re-injury and optimizing their performance.
References:
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. (2021). Labral Tears of the Shoulder. Retrieved from https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases–conditions/labral-tears-of-the-shoulder
- American Physical Therapy Association. (n.d.). Guide to Physical Therapist Practice. Retrieved from https://www.apta.org/guide/overview
- Mayo Clinic. (2021). Labral Tear. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/labral-tear/symptoms-causes/syc-20354858
- Sports Health. (2013). Returning to Sports After Shoulder Stabilization Surgery. Retrieved from https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3445186/
- UPMC HealthBeat. (2019). Labrum Tear of the Shoulder: What to Know. Retrieved from https://share.upmc.com/2019/08/labrum-tear-shoulder/






Leave A Comment